Consumer Guidelines on Memory Card Erasure
Data Security in Card Disposal and Transfer
[ For Reference ]
Although there are various operating systems in use, the basic concepts are similar. The explanation given here draws on examples for Windows.
Data recorded in memory on a memory card includes a file management area and actual data storage area. A common file management area is the FAT (File Allocation Table) used with the Windows® 95 operating system, Windows® 98 operating system/Windows® 98SE operating system, and Windows® Me operating system. Another is the MFT (Master File Table) used with the NTFS (NT File System) of the Windows NT® operating system, Windows® 2000 operating system, and Windows® XP operating system.
Inside a memory card, information about these files is stored as data; and commands specified for each memory card type are used to access (read, write, erase) the internal memory.
The file management area contains the file names of real data, location information indicating where the data is stored on the disk, directory names, creation dates and other such information. When Windows operations are used to move a file to the trash can icon or delete a file, this simply changes a setting in the file management area; the data itself remains. Similarly, formatting memory media erases information in the file management area but leaves the actual data area unchanged. Running a partitioning utility such as FDISK changes the partition management information but does not remove the actual data.
If the file system is like a book, the file management area is like the table of contents and the actual data area is the body. Destroying the table of contents does not affect the text body, which remains as before.
Using a FAT file system as an example, the memory design and measures for preventing data from being recovered are described next, to help understand what needs to be done to sanitize a memory card.
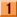 Internal Memory Format
Internal Memory Format
Internally, a memory card is generally structured as illustrated below.
Memory card internal structure
Most memory cards do not allow direct access (read, write, erase) to the internal memory. Instead, memory is accessed by means of commands to a memory card controller.
When memory is erased, the controller overwrites the memory bits with a fixed value such as FF or 00. When data is written, since generally it would be too time-consuming to first erase the existing data, in most cases the controller selects an area where the data has already been erased and writes the new data there. The controller decides to erase an area only if the existing erased area is too small. It is thus difficult to erase memory directly in ordinary access. Unless a "memory erase" command is specified as one of the memory card commands, it is not possible to erase internal memory by command.
Described next is the erasing of files on a memory card using a personal computer or the like.
How Data Is Recorded in Internal Memory (Illustration)
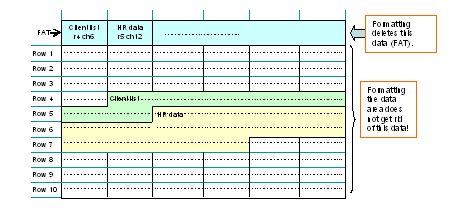
For the files in a memory card, the FAT manages the locations and areas where the data is stored.
When file management area information in the FAT is deleted, the location of data is no longer known to Windows, and the files are considered to be deleted.
Some combinations of cameras and memory cards make it possible to delete internal memory data, but for the rest the data remains.
 How Data Recovery Works
How Data Recovery Works
By analyzing data area management information still in the data area outside the remaining FAT area, it is possible to estimate the file management area information. While 100% recovery is not guaranteed, this approach to data (file) recovery is used by various software available on the market.
Such software has been developed for the useful purpose of rescuing files that the user deleted by accident. Going back to our book example, this procedure is like reconstructing the missing table of contents by looking at the chapter and section divisions along with the page numbers.
 Preventing Data Recovery
Preventing Data Recovery
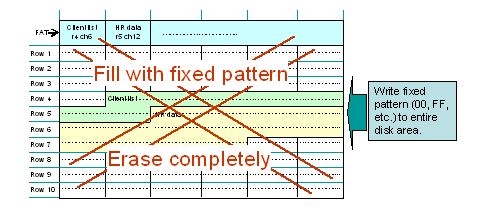
As noted above, when data in memory cannot be deleted directly, specialized data eraser software (normally sold commercially) can be used to overwrite the entire disk area with data of a fixed pattern, thereby effectively wiping out the data that was on the disk.
Features of Eraser Software
|
(a)
|
A fixed pattern is written to the entire memory area, overwriting the data that was there before and preventing it from being recovered.
|
|
(b)
|
Since this method is not dependent on the installed OS, it can be used to erase data even if the OS or files are corrupted and cannot be accessed.
|
|
(c)
|
Log information is recorded to indicate that data has been erased.
|
Methods Other than Eraser Software
|
(a)
|
Formatting in a camera (depends on the camera model and memory card type)
With some memory cards that allow direct access to internal memory, it may be possible to erase internal data by formatting the media. This is possible only if a command is provided for erasing memory data when formatting.
|
|
(b)
|
Filling up the media by shooting scenes of no importance
By shooting random scenes with a camera to fill up the memory card to the maximum number of frames, sensitive data can be overwritten. This can take considerable time if the memory card has a large capacity, and may have to be done with an AC adapter connected to avoid using up the battery.
If the file size of the frames used to overwrite the existing frames is large, it is possible that a remaining memory area smaller than this size will not get overwritten.
|
Example : If the size of one frame of 4 Mega-pixels is approx. 1 MB, filling a 128 MB memory card will require shooting 128 or more pictures. If an area smaller than 1 MB remains, it cannot be overwritten in this way.
 More Reliable Data Erasure Methods
More Reliable Data Erasure Methods
Basically, since data that was stored in the memory used in a memory card cannot be read from residual magnetism like that in a hard disk drive, the data can be erased adequately by using a data eraser program to overwrite it with a fixed pattern one time. Generally, however, erasing twice is considered to be full erasure.
In order to meet strict military-related standards, data eraser software is likely to undergo additional improvements hand-in-hand with progress in both data recovery techniques and data erasure technology.
Windows is a trademark or registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other countries.
<< Back
Top page
Next >>
©JEITA,2003
Personal Infomatization TOP /
JEITA HOME
|



